Science & Data Document Library
Science and Data Resources
EAA 2016 Precipitation in the Edwards Aquifer Region


Description: Precipitation in the Edwards Aquifer Region from 2016 Hydrologic Data Report on recharge, discharge, water levels and water quality in the Edwards Aquifer San Antonio Region
Summary:The Edwards Aquifer Authority (EAA) monitors precipitation throughout the region using a network of 74 real-time rain gauges. Rainfall data is used as input for watershed computer models that can provide estimates of monthly recharge to the aquifer. Collected over several years or decades, the extensive database of rainfall information can also be useful for monitoring climate trends, evaluating relationships between rainfall and aquifer levels, or for understanding how global-scale phenomena such as El Nino (which refers to aboveaverage sea surface temperatures in the equatorial region of the Pacific Ocean) may affect rainfall in Central Texas.
EAA Hydrologic Data Report 2016 Discharge


Description: Hydrologic Data Report 2016 Discharge from 2016 Hydrologic Data Report on recharge, discharge, water levels and water quality in the Edwards Aquifer San Antonio Region
Summary:Groundwater discharges from the Edwards Aquifer either as springflow or as pumping from wells. Comal and San Marcos springs, the largest and secondlargest springs in Texas, respectively, are fed by the Edwards Aquifer. This springflow greatly benefits the recreational economies in New Braunfels and San Marcos, and both springs provide habitat for threatened and endangered species. Figure 1 shows locations of the major springs in the Edwards Aquifer region. Wells drilled into the Edwards Aquifer throughout the region provide water for many diverse uses, including irrigation, municipal water supplies, industrial applications, and domestic/livestock consumption.
EAA 2016 Water Quality Summary


Description: Water Quality Summary from 2016 Hydrologic Data Report on recharge, discharge, water levels and water quality in the Edwards Aquifer San Antonio Region
Summary:The purpose of EAA's water quality program is to monitor the quality of water in the aquifer by sampling streams, wells, and springs across the region for a variety of parameters. Stream sample locations, upstream of the recharge zone, monitor the quality of water entering the aquifer. Well samples are located throughout the recharge and artesian zones so that the water quality can be monitored within the aquifer. Spring samples monitor the quality of water flowing out of the aquifer. EAA's sampling program provides a representative snapshot of water quality conditions relative to the location, time, and date that the sample was collected. The Edwards Aquifer is a karst groundwater system that was formed by the dissolution of limestone rock by carbonic and sulfuric acid. Dissolution occurs when slightly acidic rainwater dissolves the limestone and creates caves and sinkholes. Sulfuric acid has a deep aquifer source, and dissolution generally occurs along the saline water/freshwater interface. These two processes significantly enhance the permeability of the Edwards Aquifer. The aquifer is characterized by rapid recharge and groundwater velocities in the recharge zone, highly productive wells in the artesian zone, and large springs, e.g., Comal and San Marcos springs.
2015-2014 Hydrological DatabReport


2015-2014 Hydrological Data Report Appendix C


EAA Hydrologic Data Report 2016 Recharge


Description: Hydrologic Data Report 2016 Recharge from 2016 Hydrologic Data Report on recharge, discharge, water levels and water quality in the Edwards Aquifer San Antonio Region
Summary:Recharge to the Edwards Aquifer originates as precipitation over the drainage area and recharge zone of the aquifer or as interformational flow from adjacent aquifers. The EAA maintains a joint funding agreement with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) to provide surface recharge estimates for eight of the nine major drainage basins with streams that flow on to the Edwards Aquifer recharge zone (Figure 1). Recharge is estimated using a water-balance method that relies on precipitation and streamflow measurements across the region. Based on the USGS methodology, the Guadalupe River Basin does not appear to provide significant recharge to the Edwards Aquifer, so recharge is not estimated for that drainage basin.
2016-2015 Hydrological Data Report

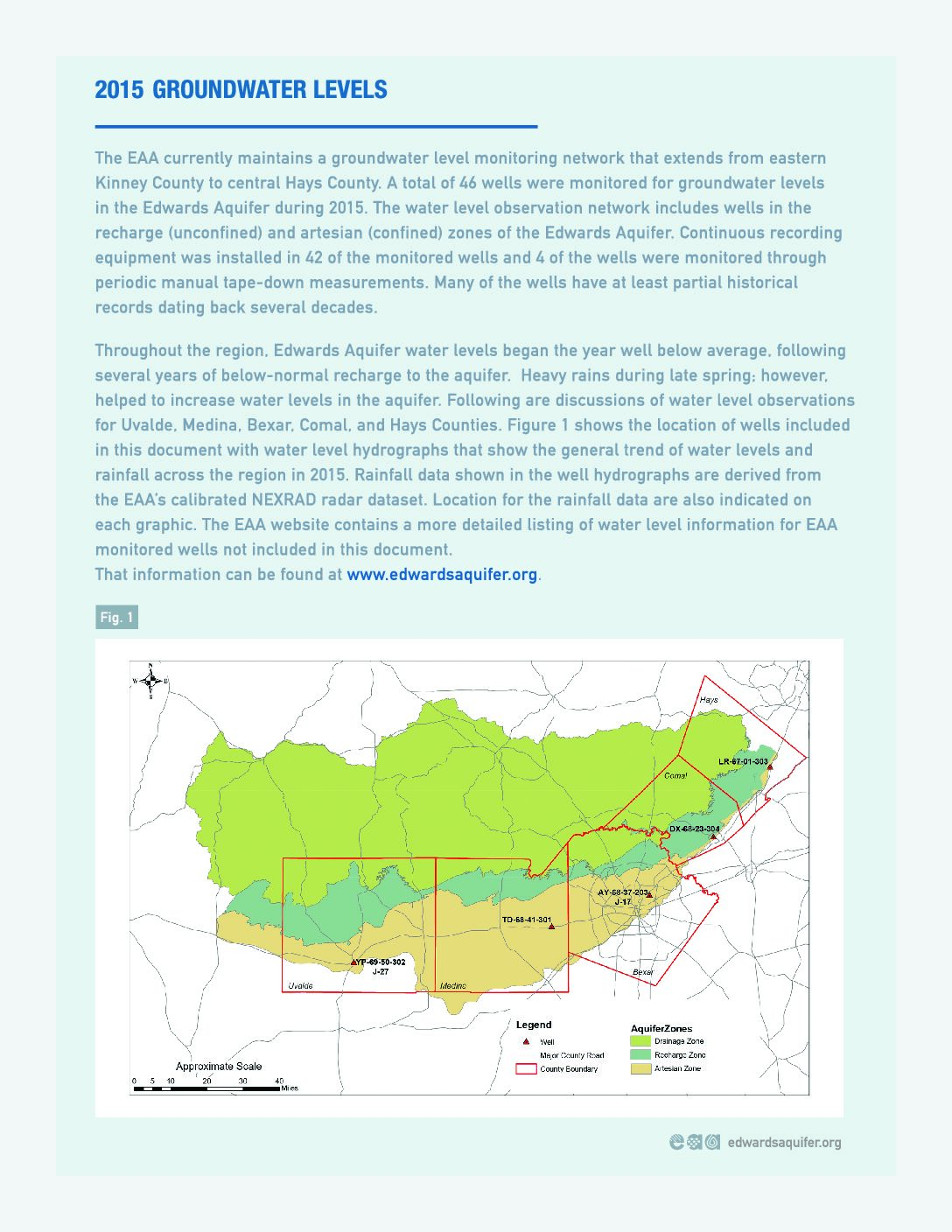
2014-2013 Hydrological Data Report


2011-2010 Hydrological Data Report


2010-2009 Hydrological Data Report


2012-2011 Hydrological Data Report


2009-2008 Hydrological Data Report

2007-2006 Hydrological Data Report


2008-2007 Hydrological Data Report


2006-2005 Hydrological Data Report


 Conditions
Conditions

 CURRENT
CURRENT 
